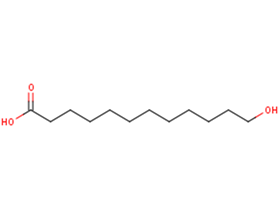
12-Hydroxydodecanoic acid
CAS No. 505-95-3
12-Hydroxydodecanoic acid( 12-hydroxylauric acid )
Catalog No. M19613 CAS No. 505-95-3
12-hydroxydodecanoic acid is the substrate of the human glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 72 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 125 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name12-Hydroxydodecanoic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description12-hydroxydodecanoic acid is the substrate of the human glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase.
-
Description12-hydroxydodecanoic acid is the substrate of the human glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms12-hydroxylauric acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number505-95-3
-
Formula Weight216.32
-
Molecular FormulaC12H24O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESOCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Sanghani PC et al. Human glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase. Structures of apo binary and inhibitory ternary complexes. Biochemistry. 2002 Sep 3;41(35):10778-86.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dihydroseselin
Dihydroseselin is a coumarin derived from the roots of Toddalia.
-
AST5902 mesylate(241...
AST5902 mesylate is principal metabolite of Alflutinib in vivo. AST5902 mesylate exerts antineoplastic activity.
-
Thiocolchicoside
Thiocolchicoside (Muscoril, Myoril, Neoflax) is a muscle relaxant with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


